Post Views: 1,991
Over the years in-memory computing has evolved and played a significant role in modern architecture primarily as part of Data Platform solutions. In-memory data grid and in-memory database/datastore technology are part of the data platform ecosystem. Click here to read the previous article on the importance of caching and in-memory data grid technology.
Context
Before we deep-dive into the decision tree to make the selection, here is the definition of both the terminologies:
- In-memory database/datastore: A database technology relying on memory (RAM) for data storage and retrieval instead of disk-based access (SAN or NAS). The primary purpose is to provide faster access to underlying data with minimal latency. To avoid loss of data stored in memory, it supports storing data on disk for long-time storage mostly using asychronous mechanism and also implements patterns to prevent failure providing high availability.
Applicability: In-memory databases are suitable for applications that require faster (micro or nanosecond) response times and need support to handle large spikes in user traffic such as gaming applications, shopping carts/session stores, and real-time analytics. - In-memory data grid: It extends in-memory datastore to distributed computing architecture with clustered computers to provide pooled storage with minimal latency and higher scalability for building and running large-scale applications.
Applicability: When building modern and high performance systems that require superior scalability, performance and low-latency and required for mission-critical applications like trading application, real-time analytics, machine-learning applications, customer data platforms, etc.
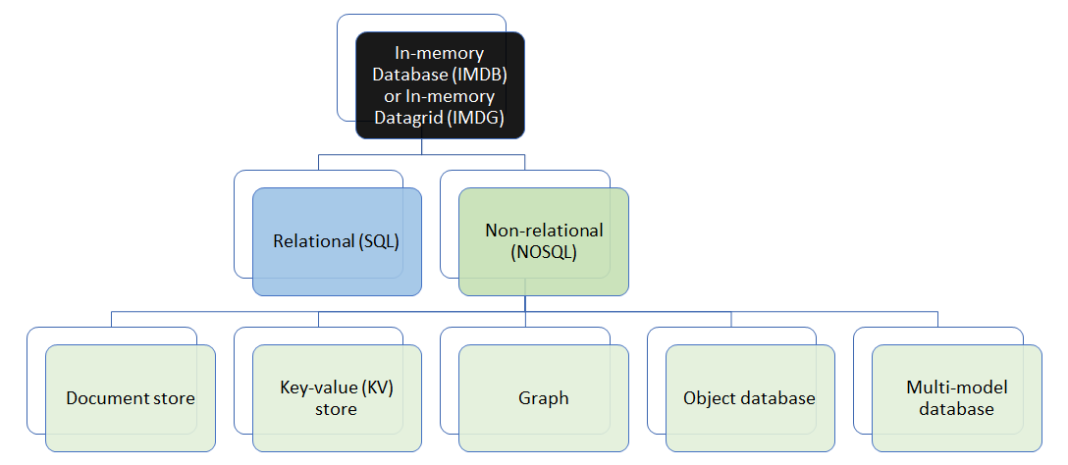
Furthermore, in-memory database or data grid products can be both relational or non-relational (NOSQL) and also can fall into any of the below NOSQL database types:
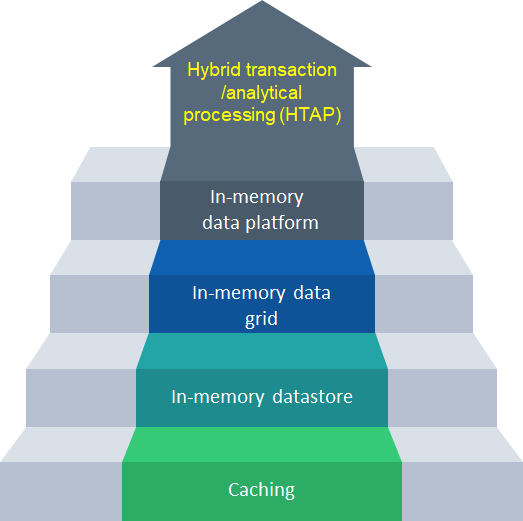
The Evolution
The below diagram depicts the overall evolution from the initial stages of caching the data towards the current state of real-time data storage and processing using in-memory data grid technology:
Gartner has coined Hybrid transaction/analytical processing (HTAP) as the next evolution of the in-memory data grid architecture, which combines the power of in-memory data store with analytical processing for real-time analytics with low latency.
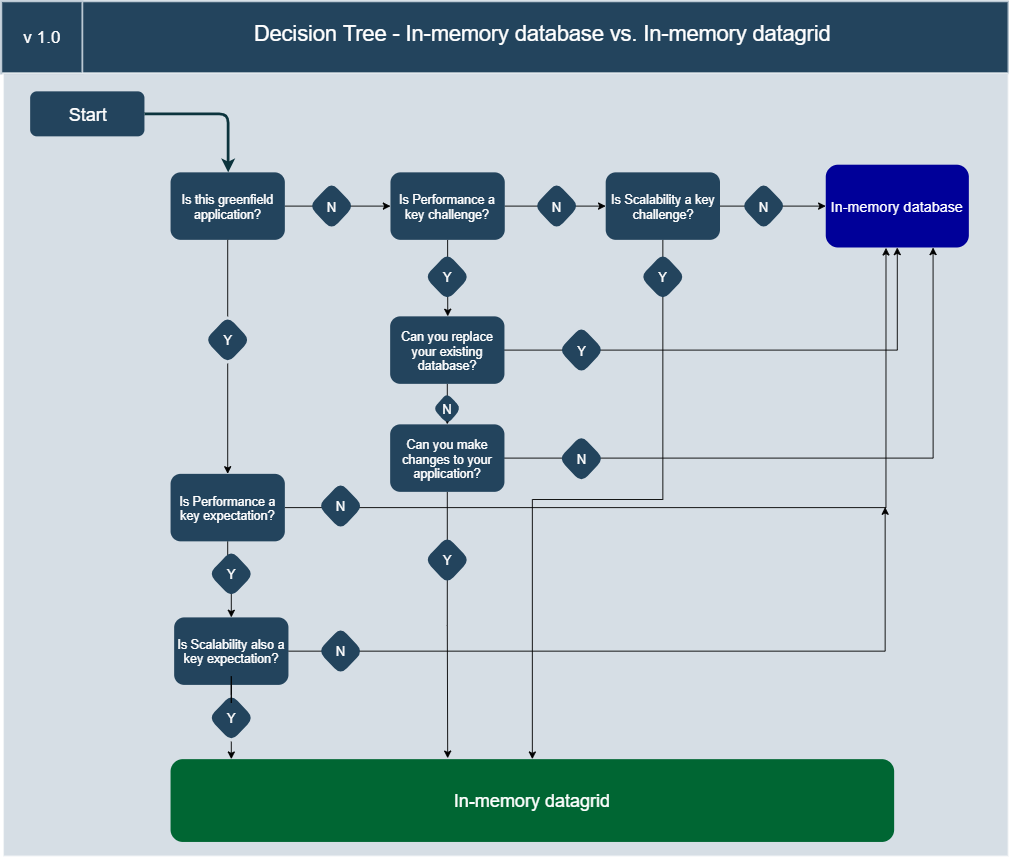
Decision Tree to choose between IMDB vs. IMDG
While in-memory data grid and HTAP technology is at the advanced level, you can start with caching and in-memory database or datastore based on your requirement. The below diagram helps to choose between in-memory datastore vs. in-memory data grid:
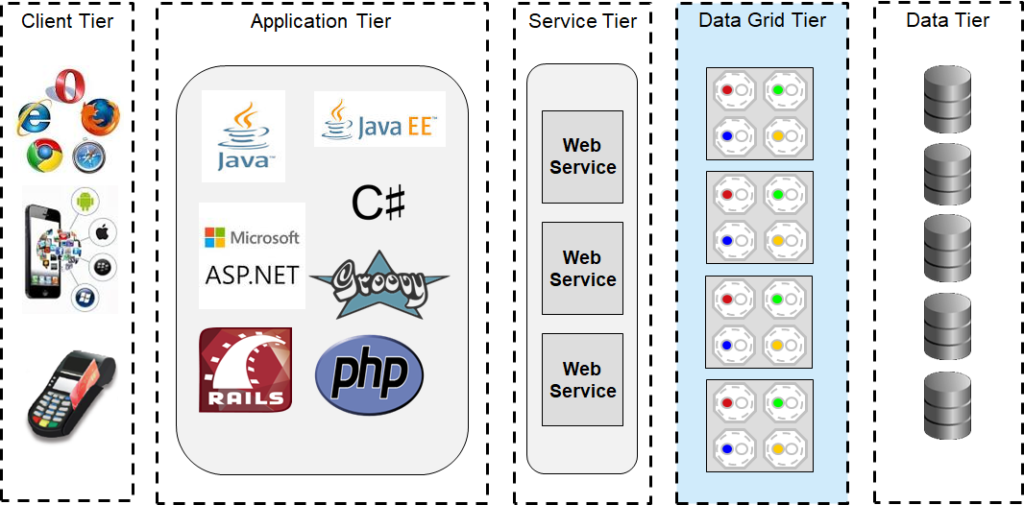
Architecture Tier
The below architecture diagram depicts, In-memory data grid placement in a typical architecture pattern.
Key difference in terms of architecture tier placement is in-memory data grid is a separate tier whereas in-memory database/datastore is part of data tier (replaces the existing data storage technology).
Product Offerings
Most of the in-memory data grid products offer an in-memory database as a core component or as a separate product itself (based on licensing and other aspects). However, there are also pure-play products, which provide in-memory database or datastore as a key capability.
The below diagram depicts key product offerings as two categories, but most of these products have evolved from just in-memory storage towards data grid as a data platform:

References
Disclaimer:
All data, images, vendor logs, and information provided on this site are for informational purposes only. This site makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, correctness, suitability, or validity of any information on this site and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. All information is provided on an as-is basis. This is a personal weblog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer or any other organization.