Tail spend (or long tail spend), often dismissed as inconsequential, can quietly erode an organisation’s bottom line. This seemingly minor expenditure on low-value, high-volume items can quickly spiral into a significant financial burden if left unchecked. In the fast-paced, detail-oriented and cost-conscious world of engineering, procurement teams should focus on addressing and implementing a tail spend management program.
The implications of unmanaged tail spend extend far beyond financial loss. It can impact project timelines, compromise quality and hinder innovation. By diverting resources from critical engineering initiatives, tail spend can stifle growth and competitive advantage.
This article delves into the hidden costs of tail spend in the engineering sector and provides actionable strategies to reclaim control. By harnessing the power of data analytics and implementing effective procurement processes, engineering organisations can unlock substantial cost savings and optimise their operations.
- Tail spend in engineering can significantly impact project budgets, timelines and quality.
- Unmanaged tail spend can divert resources from critical engineering initiatives.
- Gaining visibility into tail spend is crucial for identifying potential cost savings.
- Implementing effective key procurement processes is essential for controlling tail spend.
- Data analytics can be a powerful tool for uncovering hidden costs within tail spend.
What Is Tail Spend?
Tail spend refers to the portion of an organisation’s expenditure that is made up of high-volume, low-value, one-off purchases and transactions. Typically accounting for one-off purchases or 80% of transactions but only 20% of total spend (Pareto Principle), it often involves purchases made outside of formal procurement processes, otherwise known as “rogue spending.”
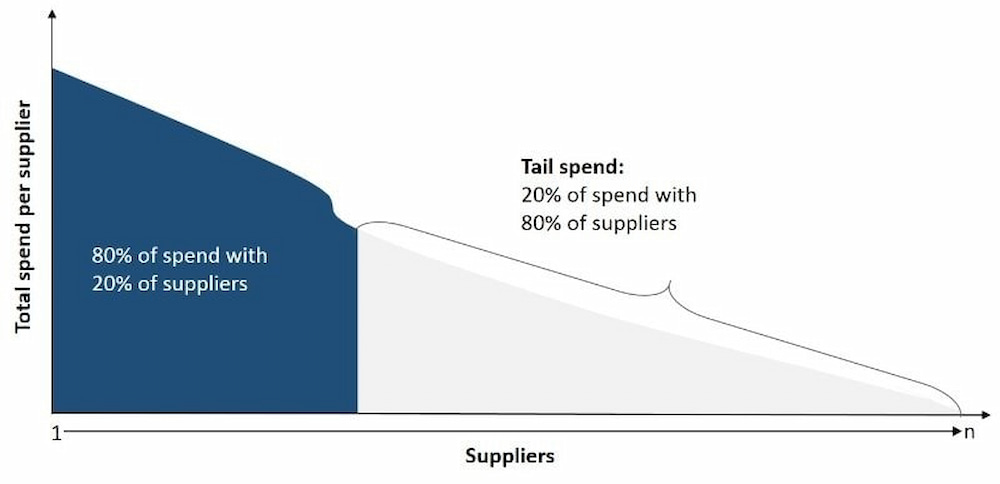
This category of spending can encompass a wide range of items, from office supplies and IT equipment to maintenance services and professional fees. Due to its fragmented nature and insignificance, it is frequently overlooked and poorly managed.
Despite its seemingly insignificant nature, the cumulative impact of rogue spending can be substantial. By understanding the strategic importance of addressing this area and conducting analysis, organisations can uncover significant cost-saving opportunities and improve overall procurement efficiency.
The Impact of Tail Spend on Engineering Projects
Unmanaged tail spend can have far-reaching consequences. This can ultimately hinder growth and competitiveness through examples such as:
Benefits of Proper Tail Spend Management
Effective tail spend management offers numerous advantages:
-
Cost Reduction: Consolidating low-value purchases, significant cost savings can be achieved through volume discounts, price negotiations, and eliminating unnecessary spending.
-
Improved Efficiency: Streamlined procurement processes and reduced maverick spending free up valuable resources, allowing teams to focus on core engineering activities.
-
Enhanced Visibility: Greater spend awareness and improved data quality can provide valuable insights into spending habits and opportunities for optimisation.
-
Risk Mitigation: Centralising procurement and working with approved suppliers reduces the risk of fraud, supply chain disruptions, and quality issues.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: Comprehensive spend data enables informed decision-making, allowing organisations to identify cost-saving opportunities and allocate resources effectively.
-
Improved Compliance: Implementing standardised procurement processes ensures adherence to company policies and regulatory requirements.
Strategies for Taming Engineering Tail Spend
Strategies to manage tail spend requires a structured approach that combines data analysis, process optimisation and supplier management. By implementing the following strategies, procurement departments can significantly reduce their exposure to hidden costs.
Spend Analysis and Categorisation:
-
Conduct a thorough analysis of historical procurement spend data to identify high-value, low-volume items contributing to tail spend, consider the Pareto principle.
-
Categorise spend based on factors such as supplier, product category, and spend volume.
-
Prioritise categories for targeted intervention based on their impact on overall costs.
Improved Procurement Processes:
-
Implement robust procurement processes to capture all spending, including low-value items.
-
Establish clear purchasing guidelines and authorisation levels to reduce maverick spending.
-
Encourage the use of preferred suppliers and contract management to leverage economies of scale.
Supplier Relationship Management:
-
Build strong relationships with key suppliers to negotiate better terms and conditions.
-
Consolidate supplier base to reduce transaction costs and increase bargaining power.
-
Explore opportunities for collaboration and innovation with strategic suppliers.
Data-Driven Decision Making:
-
Utilise data analytics tools and digital platforms to identify spending patterns, track transactions and anomalies.
-
Leverage predictive analytics to forecast future spend and optimise inventory levels.
-
Use data to measure the impact of tail spend reduction initiatives.
Category Management:
-
Establish dedicated category managers for high-spend categories within tail spend.
-
Conduct regular market analysis and supplier performance evaluations.
-
Develop category strategies to optimise spend and reduce costs.
By implementing these strategies, it is possible to gain control over tail spend, improve financial performance, and improve internal processes to enhance operational efficiency.
-
Personal account manager
-
Quality assurance
-
Payment terms for companies
-
On-time delivery by Fractory
Get a quote
Case Studies: Engineering Organisations That Conquered Tail Spend
Here are a few examples of organisations that have effectively tackled tail spend:
Case Study 1: Aerospace Engineering Firm
A leading aerospace engineering firm implemented a program to reduce costs and improve operational efficiency. By leveraging advanced data and spend analysis, they identified significant savings opportunities in indirect spend areas such as MRO supplies, office equipment and IT services. By consolidating suppliers the firm achieved a 15% reduction in tail spend within the first year.
Case Study 2: Civil Engineering Contractor
A large civil engineering contractor faced challenges with maverick spend on construction materials, equipment rentals and subcontractor services. By implementing a cloud-based P2P platform and integrating spend analytics with project management systems, they gained visibility into spending patterns, payment terms and identified opportunities for potential cost savings. Through supplier negotiations and cost-saving strategies, the contractor reduced tail spend by 10%, improving project profitability.
Case Study 3: Automotive Engineering Company
An automotive engineering company sought to streamline its processes and reduce costs associated with tail spend on engineering tools, software and consumables. By the procurement department implementing a purchase-to-pay solution and establishing clear purchasing guidelines, the company achieved a 20% reduction in tail spend and improved compliance.
Challenges of Implementing Tail Spend Management in Engineering
While the benefits of effective tail spend management are clear, engineering organisations often face unique challenges in implementing successful strategies to manage tail spend.
Data Quality and Accessibility: Engineering environments often generate complex and fragmented data, making it difficult to accurately capture and analyse a company’s spend information. Inconsistencies in data formats, missing information and disparate systems can hinder effective analysis.
Decentralised Decision Making: The nature of engineering projects often involves multiple stakeholders with a number of suppliers and varying levels of authority. This can lead to maverick spending and difficulty in enforcing procurement policies and moving towards strategically managed spend coverage.
Rapid Technological Advancements: The engineering sector experiences rapid technological changes, which can impact the types of goods and services required. This dynamic environment can make it challenging to maintain up-to-date supplier information and category management strategies.
Complex Supply Chains: Engineering projects often involve intricate supply chains with numerous suppliers, making it difficult to gain visibility and control over tail spend.
Project-Based Nature of Work: The project-based nature of engineering work can create challenges in managing tail spend, as spending patterns may fluctuate significantly over time.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of technology, process improvement and change management.

It’s time to take action. Identify the low-hanging fruit and implement quick wins to reduce costs immediately. Invest in key procurement processes, technology and data analytics to gain deeper insights into your spending patterns. Build strong relationships with key suppliers to negotiate better terms. And most importantly, empower your procurement team to drive change.
By taking decisive steps to manage your tail spend, you can unlock significant savings, gain a key competitive advantage, improve operational efficiency, and position your engineering business for long-term success.